The idea that today’s powerful Large Language Models (LLMs)—like the GPT series or Gemini—are simply “Cleverbot 2.0” is a fascinating thought that captures the rapid evolution of conversational AI. But is it accurate to call Cleverbot the origin of current LLMs?
The relationship is more like an ancestral connection within a complex family tree of Artificial Intelligence, rather than a direct parent-child relationship.
1. The Early Ancestors: Rule-Based Systems (The Pre-Cleverbot Era)
The history of conversational AI begins long before Cleverbot. Its earliest predecessors were not statistical prediction engines but rather rule-based systems:
- ELIZA (1966): Created by Joseph Weizenbaum, this was one of the first programs to simulate conversation. It used simple pattern matching and substitution rules (like a Rogerian psychotherapist) but had absolutely no understanding of the text. It set the baseline for what a believable human-computer dialogue could feel like.
2. The Contextual Leap: Cleverbot and Statistical Retrieval
Cleverbot, launched in 2008 (preceded by the Jabberwacky project starting in 1988), marked a significant step beyond simple rule-based systems. Cleverbot’s core innovation was its method of generating responses:
- A Database of Human Conversation: Instead of relying on a human programmer to write rules, Cleverbot used a massive database of previous human-to-Cleverbot interactions.
- Response Retrieval: When a user typed an input, Cleverbot didn’t generate a new response; it searched its database for the closest matching human input and returned the human response that followed it. It relied on a form of machine learning to choose the best-fit response.
In this sense, Cleverbot was a pioneer in using real-world human data to drive conversation, creating a more unpredictable and human-like dialogue than its predecessors.
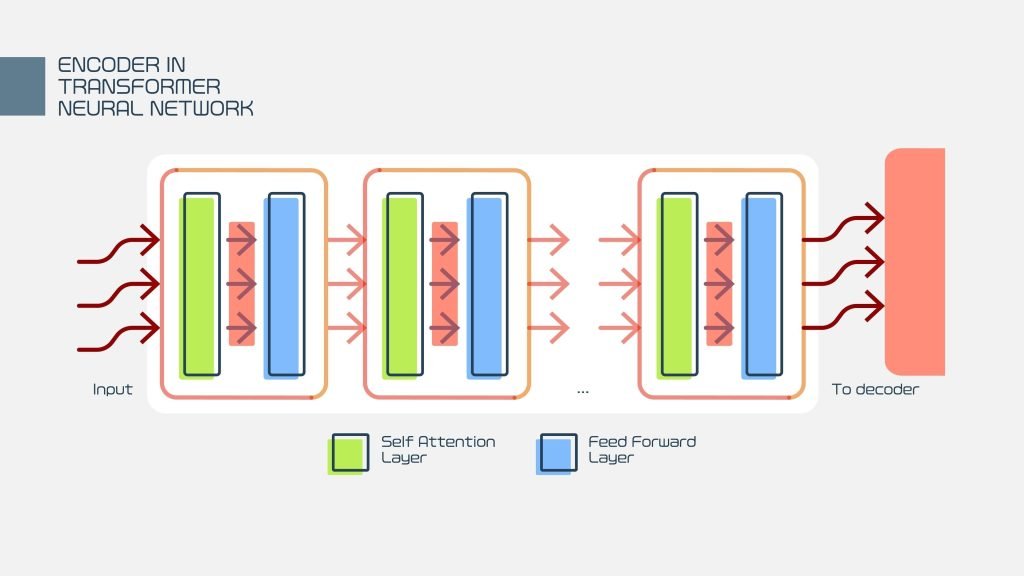
3. The True Foundation: Deep Learning and the Transformer Architecture
While Cleverbot provided a highly engaging conversational experience, the modern LLM technology rests on an entirely different architectural foundation that truly represents the “origin” of their current power:
| Architecture | Cleverbot/Jabberwacky (Statistical Retrieval) | Modern LLMs (Deep Learning/Transformer) |
| Core Mechanism | Retrieval and matching of pre-recorded human responses. | Generative—predicts the next statistically probable token (word/sub-word) in a sequence. |
| Foundation | Large, searchable database of conversations. | Transformer Architecture (introduced by Google in 2017), using self-attention mechanisms. |
| “Intelligence” | Mimicry of past human exchanges. | Learned patterns, grammar, semantics, and context from training on trillions of tokens of text and code. |
| Scale | Millions of conversations. | Billions to Trillions of parameters. |
The key breakthroughs that separate today’s LLMs from Cleverbot were:
- Deep Learning (1990s – 2010s): The shift to neural networks, especially deep neural networks, allowed models to learn hierarchical features from data instead of just surface patterns.
- The Transformer (2017): This architecture revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP). It allowed models to process vast sequences of text in parallel and capture long-range dependencies, making them exponentially faster and more powerful to train on truly massive datasets.